
Gene allows beta cells to ‘communicate’ release of insulin
Diabetes, which affects millions of people worldwide, develops when the body either generates insufficient amounts of the hormone insulin – a hormone that maintains healthy blood sugar – or when the body cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. When the number of beta cells is too low or they aren’t functioning properly, there isn’t enough insulin getting released.
Beta cells communicate with each other to secrete insulin in a co-ordinated manner. An international team of scientists from the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) in Dresden, Germany, the Paul Langerhans Institute Dresden (PLID), and the Universities of Oulu, Finland and Copenhagen, Denmark now shows that the gene Wnt4 in beta cells enables them to sense glucose and release the hormone insulin that enables other cells in the body to store glucose.
These insights could help to create replacement beta cells for diabetes therapy in the future.
See also: Drug discovery method finds natural metabolite that changes ‘bad’ fat to ‘good’
beta cells in the pancreas
At birth, a baby starts to eat food and turns it into energy. Many nutrients can be converted to sugar (glucose) and be released into the bloodstream. Higher blood sugar levels signal the beta cells in the pancreas to release insulin, which lets the blood sugar into the cells to use or store it as energy.
However, at different stages of life, the food-sensing beta cells need to adapt to different foods and needs. In a recent study Anne Grapin-Botton, director at MPI-CBG, and her team in Dresden and at the Novo Nordisk Foundation Center for Stem Cell Biology in Copenhagen, Denmark, together with colleagues from the Faculty of Medicine Carl Gustav Carus of the Technische Universität Dresden found that the gene Wnt4 becomes active in food-sensing beta cells as they mature in early postnatal life.
The discovery of the role of Wnt4 in the development of a pancreas started in the 1990s at Harvard University, when Anne Grapin-Botton, a postdoctoral researcher at that time, discussed with Seppo Vainio, now a research unit leader at the University of Oulu.
Vainio said: “I remember that when I worked with Wnt4 in kidney development, we speculated that this signal would have a role in the development of the pancreas too.”
But the researchers were lacking the right tools at that time. Over 20 years later, postdoctoral researcher Keiichi Katsumoto, in the lab of Anne Grapin-Botton, was keen on finding out what function the gene Wnt4 has in pancreas development.
In the meantime, the lab of Vainio at Oulu had further developed their mouse models. Vainio said: “With all these tools, we could target Wnt4 function in pancreas development and physiology with Anne Grapin-Botton’s research lab.”
less insulin
Keiichi Katsumoto describes what he observed: “We found that the gene Wnt4 is expressed in beta cells during the maturation of the cell. The cells that start expressing Wnt4 stop proliferating and become more functional. We saw that with less Wnt4, the beta cell secretes less insulin.”
The team found that even though the beta cells were able to detect sugar in the blood, they secreted less insulin in response to glucose.
Grapin-Bottin, who supervised the study, added: “When we saw that mice without the gene Wnt4 were becoming diabetic, we knew we had found something important, but we did not understand how it was acting.
“We understood from work in other organs, notably our collaborator Seppo Vainio and his colleagues, that this gene is a signal sent by cells to others. It was exciting to find communication between beta cells in the pancreas, its conservation across several animal species and the mechanisms by which it operates, notably the profound metabolic changes it provokes in beta cells.
“However, we do not understand yet if beta cells release Wnt4 constantly or under special circumstances. This will be something, we want to explore in the future.”
Katsumoto stated: “The results also suggest that the increase of Wnt4 shortly after birth enables beta cells to mature. Our next step is to understand why Wnt4 becomes expressed as the cells mature.”
Those results could support the development replacement beta cells for diabetes therapy with added Wnt4 to promote maturation.
The research is published in Nature Communications.
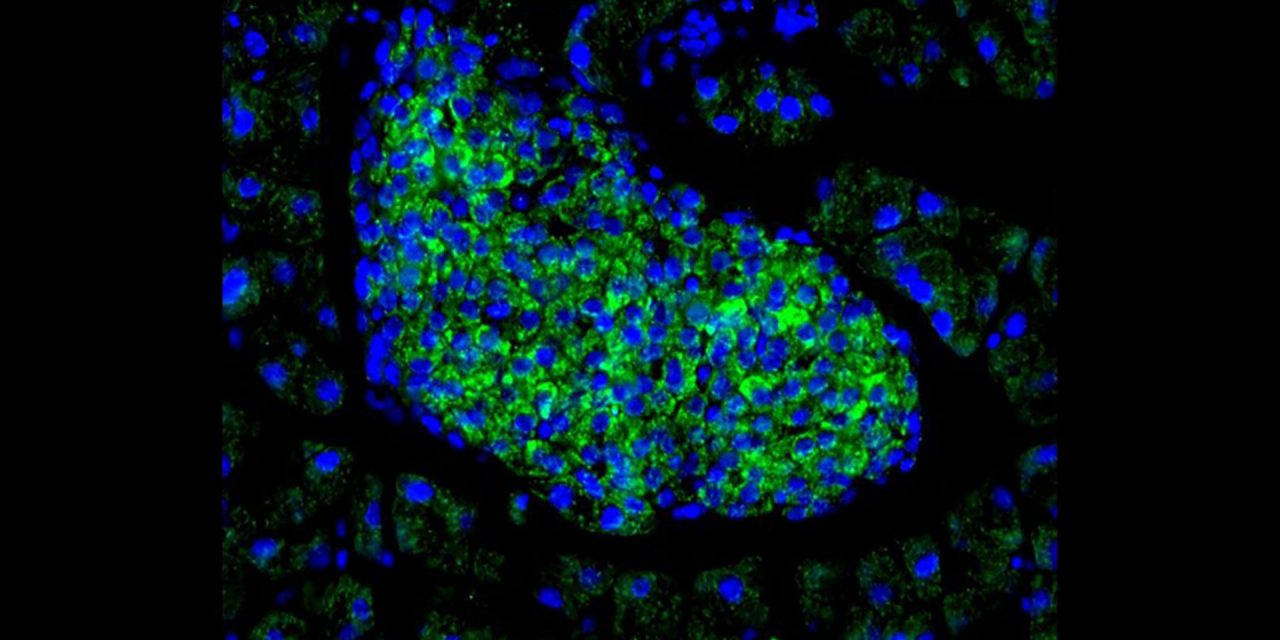
Islet of Langerhans with the Wnt4 staining in green and the cell nuclei in blue. © Katsumoto et al.















